This episode of CS is titled Awakening.
The tide of Pietism that swept portions of Europe in the 17th C, arrived in North America in the 18th. Like the Charismatic Movement of the 1960s, Protestant denominations were split over how to respond to Pietism. Presbyterians were divided between those who insisted on strict adherence to the teachings of the Westminster Confession and those whose emphasis was on having an experience of saving grace. The two sides eventually reunited, but not before the contention became so sharp, it led to a rift. That reached its zenith, or nadir might be a better descriptive, during The Great Awakening.
As we saw in our last episode, the Half-Way Covenant of New England allowed people to be members of the Church, without being saved; a formula for disaster. The Half-Way Covenant, along with the assault of the pseudo-intellectualism of the Enlightenment, resulted in a creeping spiritual lethargy among the churches of the English colonies. Jonathan Edwards, who became one of the main luminaries of The Great Awakening, remarked before it began that the spiritual condition of New England was abysmal.
The first stirrings of revival began as movements in local churches five to ten years before the Great Awakening. There’d even been some minor revivals in Northampton during the time of Edwards’ grandfather, Solomon Stoddard in the 1720s.
Theodore Frelinghuysen was a Dutch Reformed pastor who’d come to North America to pastor four churches in New Jersey. Frelinghuysen was what’s called a Precisionist, a Dutch version of an English Puritan. Puritanism was exported to Holland by William Ames where it was referred to as Precisionism.
Pastor Frelinghuysen discerned a general spiritual malaise in all four of his congregations there in New Jersey; an appalling lack of practical piety. So he decided to embark on a program of reform. He started visiting people in their homes. He enforced church discipline and preached fervent evangelistic sermons. A few opposed these innovations, but he persevered and the churches began to grow with genuine conversions resulting in a warming up of the entire congregation in their fervency for the things of God. It was the first stirrings of revival, which spread to other Dutch Reformed churches. By 1726, Frelinghuysen was recognized as a leader of revival.
The Presbyterians of New Jersey saw what was happening among their Dutch neighbors and soon joined the revival under the work of the father and son team, William and Gilbert Tennent.
But when it comes to The Great Awakening, the name most closely associated with it is Jonathan Edwards.
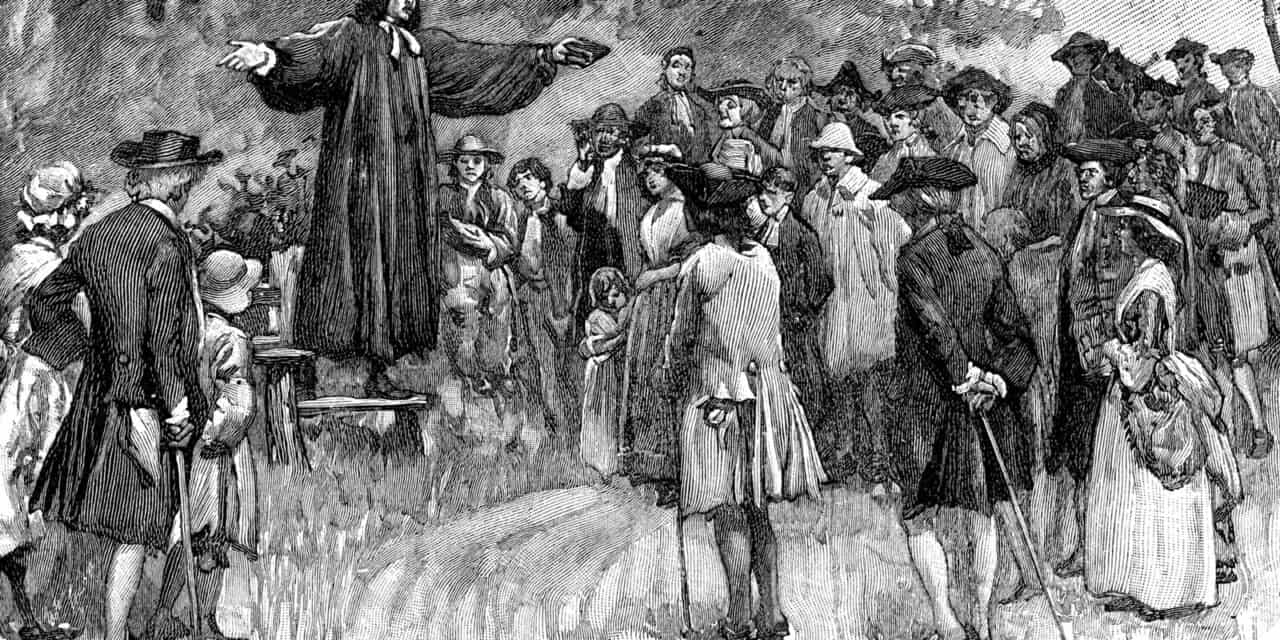
Edwards is considered by many to be one of the most brilliant minds in American history. He wasn’t just a great theologian. He was a top-rank philosopher and scientist. Edwards is sometimes presented as a fiery preacher in the Puritan vein. The popular notion of him is that he was a revivalist-preacher of a mien similar to George Whitefield. His most famous sermon was Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God. The title alone gives one the impression of a wild-eyed and crazy-haired pulpit-pounder. But that image is far from what Edwards was really like. He was reserved and tended toward shyness. He was more at home in his study among his books than in a pulpit. Edwards spent ten hours a day studying. His messages were filled with theology and their delivery was not the kind of fire and brimstone preaching many assume. His style was to virtually read his messages. That’s not to say his delivery was wooden, but descriptions of it remarked on the lack of gestures or inflection of voice. Flamboyance was nowhere in sight when Edwards spoke. He trusted in the eloquence and logic of his message to persuade, rather than by affecting a dramatic persona. If there was grandeur in his message, it was due to WHAT he said, rather than in HOW he said it.
Edwards was a PK; a pastor’s kid. His father Timothy was a minister in the town of East Windsor, Connecticut. By the age of thirteen, he’d master Greek, Hebrew, and Latin. He wrote essays on scientific matters and penned one on the behavior of insects that became famous. As a teen, he read and consumed the ideas of Sir Isaac Newton. He graduated from Yale at seventeen.
It was during his college years his relationship with God deepened into rich intimacy. All of that grew out of the time he spent studying the nature and character of God.
Edwards added two more years of post-graduate studies then took a pastorate at a small church in New York for only a couple of months. That was followed by a stint as a tutor at Yale for another two years. In 1727, he became an assistant pastor to his grandfather, Solomon Stoddard at Northampton, Mass. Also at that time, he married Sarah Pierpont.
When Edwards took up his ministry at Northampton in 1727, he found the church to be spiritually dull, even though it had been the scene of earlier stirrings of the Spirit under Stoddard’s leadership. When Stoddard died in 1729, Edwards stepped into the role of senior pastor.
He decided to address the spiritual apathy of the congregation by preaching a series of five sermons on justification by faith. He rightly diagnosed the real problem at Northampton wasn’t laziness or moral sloppiness; it was an absence of good theology. Instead of preaching the need for repentance and obedience, he focused on the glory of God in the Gospel of Christ. Sure enough, a season of renewal came as people recommitted themselves to follow Jesus. The messages weren’t calculated to elicit an emotional response, but they did. People responded with a remarkable moral and spiritual change, often with intense emotion.
After several months, the movement spread thru out Massachusetts and into Connecticut. After three years it began to diminish. But the memory of revival endured, with many hoping for it to be renewed.
In 1737, Edwards decided to pen a chronicle of what had happened over the previous three years. It was titled, A Faithful Narrative of the Surprising Work of God in the Conversion of Many Hundreds of Souls in Northampton. That’s the title; not the actual text of the whole thing. The Narrative as it’s more conveniently referred to, is what established Jonathan Edwards as the main person associated with Revival.
In 1739, George Whitefield visited New England. Though Edwards and Whitefield represented different flavors of the Faith, they were both deeply committed to the Preaching of the Gospel. Edwards helped arrange Whitefield’s campaign through the area of Boston then on to Northampton where Edwards turned his pulpit over to the great preacher. The winds of renewal that had waned a few years before strengthened once more.
Then Edwards was invited to speak at the church in Enfield, Connecticut in 1741. His message was titled, Sinners in the Hands of an Angry God. Reading the text of the sermon today one might assume it was delivered in the ham-fisted, “fire and brimstone” manner of a fanatic. But as we’ve seen, that was not Edward’s style. Nor did he deliver it in the monotone some later reports suggest. He spoke as a man convinced of his topic; urging his listeners to make sure they’d embraced the Grace of God. The sermon paints a terrifying picture of eternal damnation; something Edwards aimed to make clear. Because as historian George Marsden says, Edwards didn’t preach anything new to his hearers. They were well acquainted with the Gospel as a remedy for sin. The problem was getting them to seek it.
While revival was already building, Edwards’ sermon at that church in Enfield was a crystalizing moment in The Great Awakening. If the coals had been getting hot they now burst into flames that spread all over New England and to the other colonies, even across the Atlantic to settle in England and the Continent.
As welcome as The Great Awakening might have seemed, some ministers opposed it. Their opposition stemmed from their resistance to the emotionalism that became a mark of the Revival. People wept in repentance then shouted for joy at being saved. Some were so emotionally wrought over the process of their conversion, they fainted. A few who were psychologically fragile exhibited what can only be called bizarre behavior.
Such reactions led the enemies of the Great Awakening to accuse its leaders of undermining the solemnity of worship, and of substituting emotion for scholarship. Since it’s the tendency to stick labels on movements, supporters of the Awakening were called New Lights, while those who opposed it were called Old Lights.
Edwards made clear in his writings that he believed emotion was important. But emotion, including the intense experience of conversion, should never eclipse doctrine and orderly worship.
At first, Baptists opposed the Awakening, labeling it frivolous and superficial. But so many of the new converts were inclined to agree with Baptist positions that they ended up becoming Baptists. When the Baptists saw all these new members, their opinion of the Revival changed. Most notable was the conviction among the new converts that baptism ought to be of those who profess faith in Christ, not infants. Entire Congregationalists and Presbyterian congregations became Baptists.
The Great Awakening sent Baptists and Methodists to the Western frontier. Settlers continually pushed the Frontier westward. It was Methodist and Baptist missionaries who took up the task of preaching to them and planting frontier churches. So those two groups became the most numerous out West.
It’s difficult to estimate how many conversions took place during the Great Awakening but gauging by fairly accurate church records taken over that time indicate a conservative number of ten percent of Americans came to Faith. In some communities, it was much higher than that. Keep in mind that was in the midst of a society already considered thoroughly Christian.
Besides the obvious spiritual effects of the Great Awakening, it had a notable political impact in the British colonies of North America. It was the first movement to include all thirteen colonies. A new sense of commonality developed in which the emerging unique identity as Americans, as opposed to British, took root alongside the idea that to be an American meant to be a Christian of Protestant stripe.
The Great Awakening propelled a wave of missionary activity. David Brainerd, Jonathan Edwards, and others preached to the Indians, and some effort was made to reach blacks with the gospel. Among the colleges birthed at that time were Princeton, Rutgers, Brown, and Dartmouth. Dartmouth trained Indians to serve as missionaries to their own people.
Edwards continued in his role as pastor till 1750 when a controversy saw him removed.
Edwards believed Communion ought to be given only to those church members who’d demonstrated a genuine conversion experience, as per the Pietistic belief. His grandfather, the previous pastor, had relaxed the traditional Puritan practice and allowed what we’ll call ‘unconverted church members’ to partake of the Lord’s Supper. Stoddard regarded Communion as a “converting experience.” He thought regular attendance at the Lord’s Table would be something the Holy Spirit could use to bring conviction and salvation to a needy soul. Edwards disagreed, viewing Communion as open only to those who were converted.
By 1750, Edwards had come to this position though at odds with the tradition of the church he pastored. When he tried to implement a change in practice, they released him. Yep, they canned him. It was then that he embarked on his mission of taking the Gospel to the Indians at Stockbridge, Mass. It was while engaged in that work that he wrote his most famous work – Freedom of the Will.
I want to share a little story from the life of Jonathan Edwards that may give us some insight into the man. After fourteen years of marriage, in January of 1742, something happened to his wife Sarah. She had an intense religious experience. Some historians think it was a nervous breakdown. Edward was away on a preaching tour. His pulpit was being filled by Samuel Buell who gave a series of sermons with profound impact on Sarah. She was overwhelmed to the point of fainting. Her condition was such that she was unable to take care of her children, who were sent to stay with neighbors till John returned a few weeks later.
The town was abuzz with the nature of her condition. Was it some kind of spiritual ecstasy or an emotional breakdown? When John returned, he of course immediately went to her to see what was wrong. She related to him that she’d experienced God’s goodness as never before; as she didn’t even know was possible. She said the joy and security she now had was so intense it was at times debilitating.
John’s reaction was interesting. He affirmed she’d had a visitation from God. Keep in mind we’re talking here about hard-core, strict Calvinist; not a Pentecostal or even a more mild Charismatic.
After a few weeks, Sarah recovered and returned to the normal activities of life. But John said from then on Sarah maintained a peace and joy that transformed her. In writing about the effects of the revival, while Edwards doesn’t name his wife, it’s clear some of what he chronicled were things he witnessed in his own wife when she was filled with the Holy Spirit in 1742.
In 1757, Edwards was appointed president of Princeton, known then as the College of New Jersey. A short time later, he volunteered to be a test subject for a smallpox vaccine. Which instead of inoculating him against the disease, claimed his life in 1758.
One of my favorite teachers is J. Edwin Orr. When Orr died in 1987, he was recognized by many as the 20th Century’s foremost expert on Revival. He spent his last years living a few miles from where I am now, in CA. My good friend and fellow pastor David Guzik befriended Orr’s widow, who passed many of Dr. Orr’s books, writings, and recordings on to him for posterity’s sake. David has faithfully made that material available online at jedwinorr.com .
The eminent New Testament scholar FF Bruce said, “Some men read history, some write it, and others make it. So far as the history of religious revivals is concerned, J. Edwin Orr belongs to all three categories.”
Orr tells remarkable stories of the impact of revival on society. The many revivals he chronicles don’t merely add a bunch of new church members; they have an astounding impact in moral revolution. Orr shares that during some revivals, because there was no crime, the Police organized singing groups to sing in churches because they had nothing else to do. There were a number of business failures; pubs and other enterprises that thrive on vice folded.
One unforeseen effect during the Welsh Revival was that there was a work stoppage in the coal mines of Wales. For years, the mules that pulled the coal carts were used to hearing the miners curse at them. But when so many miners converted during the Revival, they refused to curse anymore and the mules no longer heard the profane commands telling them to move. Work in the mines stalled till the mules were retrained to respond to the now clean speech of the joyous miners.
If you’re interested in more such interesting stories, I encourage you to head over to jedwinorr.com for more.
And I want to also encourage you to check our David Guzik’s website at enduringword.com.
David is one of the premier Bible expositors online today. His free commentary is used by many thousands of pastors, professors, Bible teachers and students all over the world.
Donations of any size to CS are welcome. You can do so at sanctorum.us // Thanks.






Please forgive me for using a minor quibble to unload a criticism that I have with some other podcasters. You comment on Jonathan Edwards’ preaching style, then later when discussing his most famous sermon, you say, “But as we’ve seen, that was not Edwards’ style.” I would prefer to hear, “As I have shown, that was …”
I have heard other podcasting preachers make disputable assertions about a certain subject, then later say, “As we have seen, blah, blah, blah.”. My reaction to this rhetoric device is, “No, I do not see it that way!” The point intended could more honestly be made by saying, “As I have explained…”, or more correctly, “As I have asserted,…” Preachers are in the business of persuading, but in my opinion, they should avoid rhetorical sleight of hand in making their case. There, I have unloaded this pet peeve on someone. Please forgive me.
George,
Thank you for notifying me of your dislike of the phrase you mentioned.
I understand your point and will attempt to file it away in my leaky memory & attempt avoid using, unless of course, I believe the case HAS BEEN sufficiently made to arrive at a reasonable conclusion.
Lance